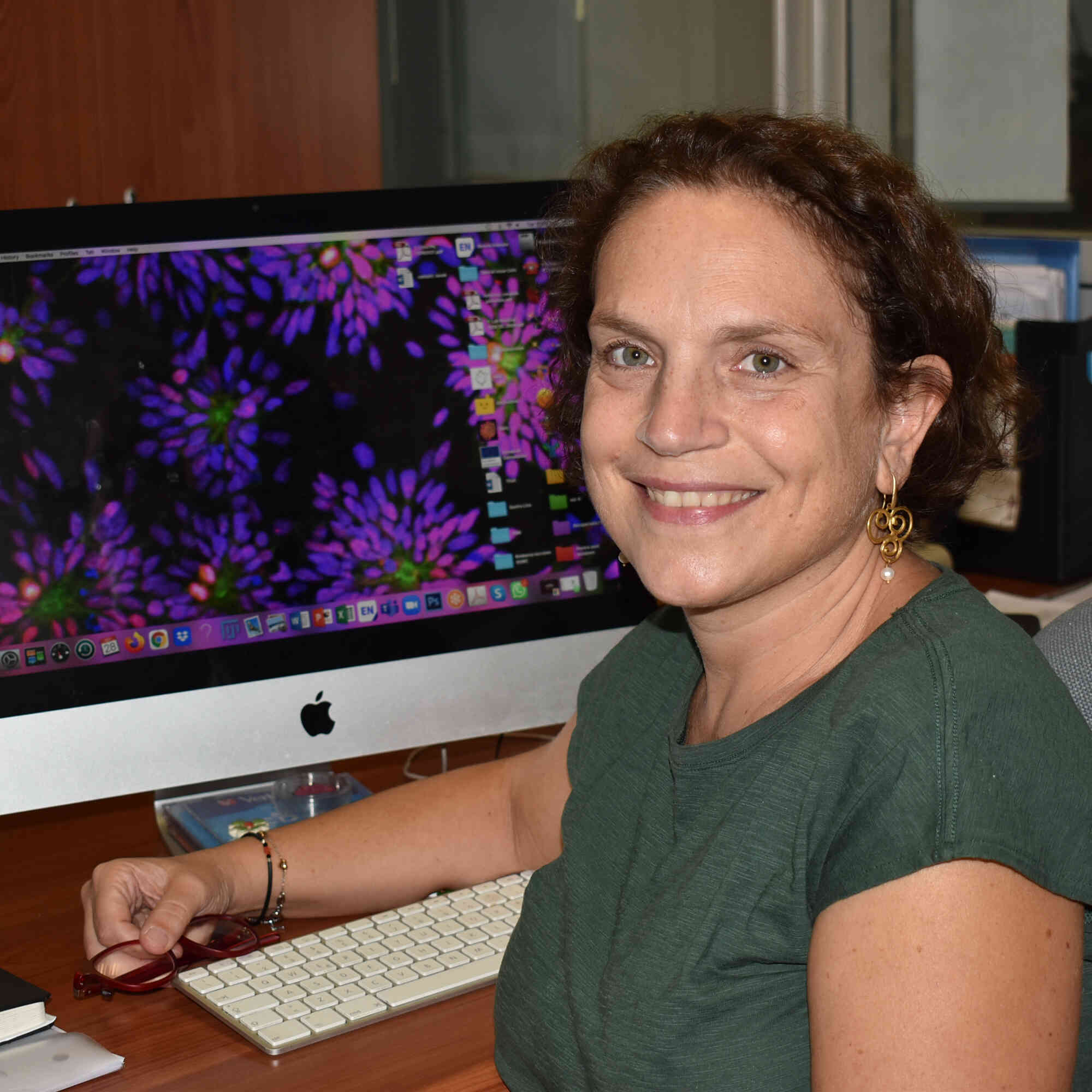
Annalisa Fico
Researcher
![]() +39 081 6132 721
+39 081 6132 721 ![]() annalisa.fico@igb.cnr.it
annalisa.fico@igb.cnr.it
Embryonic Development and Biology of Stem Cells
Keywords: Stem Cells and Pluripotency/Long Non-Coding RNA/Neural Differentiation
- Research Interest
- Selected Publications
- Professional Experience
- Associated People
Our research activity is focused on the molecular and cellular mechanisms governing cell plasticity in mammals. Among the several contexts where cellular plasticity and heterogeneity are involved, there is the stem cell biology and their application in regenerative medicine, which mainly represent our interest. We study both extracellular and intracellular control of cell plasticity, such as cell signalling, metabolism and post-trascritional regulation. In the last few years, we concentrated our attention on the family of long non-coding RNA, the Transcribed ultraconserved elements (T-UCEs). The T-UCEs exert a great interest given their full conservation among human, rat, and mouse genomes, and they have been described acting as “natural sponges” to decoy specific miRNAs. In particular we are highlighting the T-UCEs involvement in embryonic stem cells (ESCs) neural differentiation and we have identified a new lncRNA, named T-UCstem1, and provided in vitro and in vivo evidence that it plays essential roles in ESCs by modulating cytoplasmic miRNA levels and preserving transcriptional dynamics.
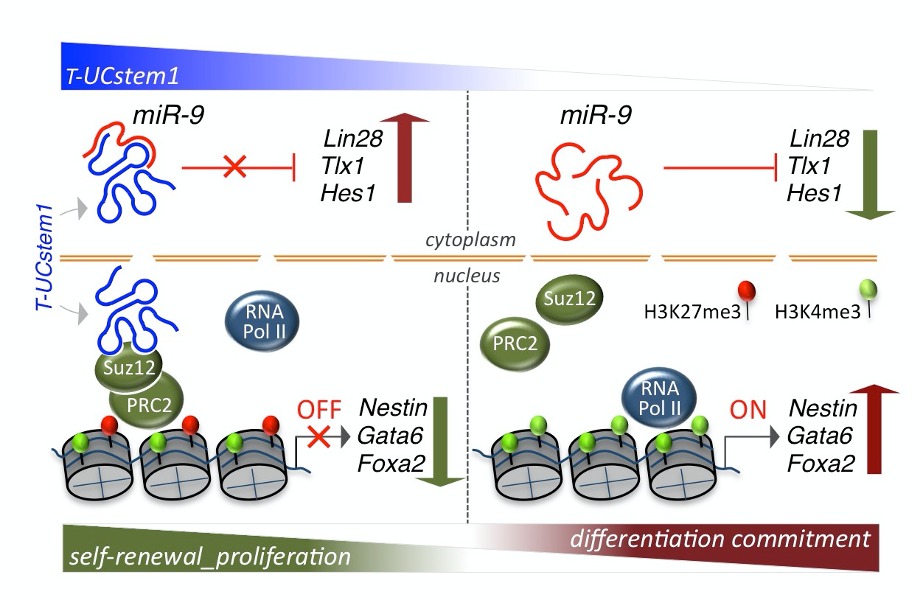
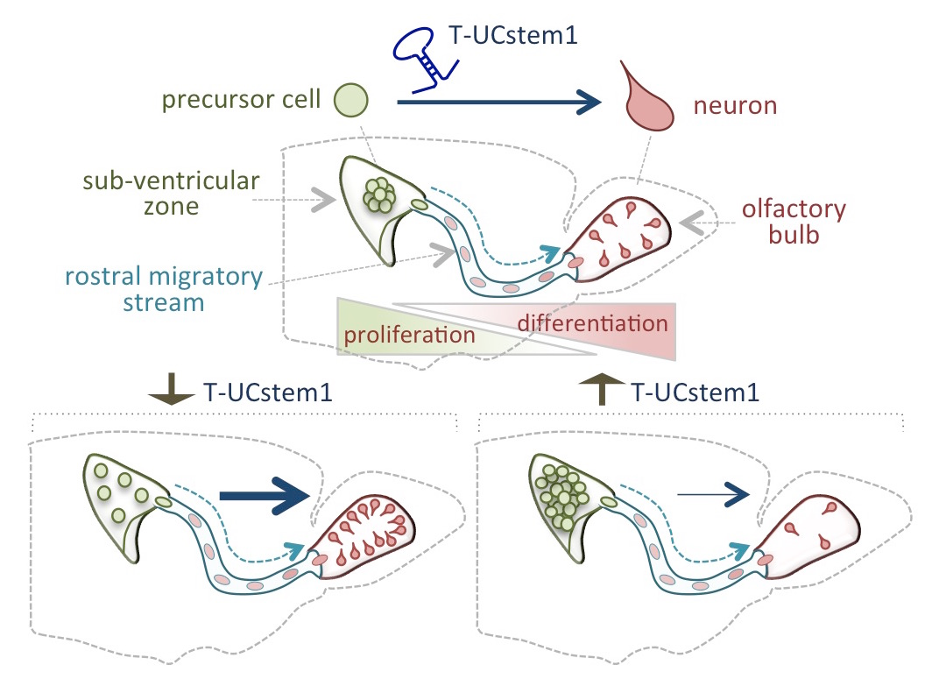
By combining gain- and loss-of-function experiments in post-natal mouse brains, we extended our studies to adult stem cells, and in particular to neural stem cells. We showed that T-UCstem1 is expressed in the forebrain neurogenic lineage that generates interneurons for the postnatal olfactory bulb. Gain of function in neural stem cells increased progenitor proliferation at the expense of neuron production, whereas knockdown had the opposite effect. This regulatory function is mediated by its interaction with miR-9-3p and miR-9-5p. Based thereon, we proposed a mechanistic model for the role of T-UCstem1 in the dynamic regulation of neural progenitor proliferation during neurogenesis.
We are also preceding our studies by further analyze T-UCstem1 function in 3D embryonic organoids/gastruloids, in human pluripotent stem cell-derived mini brains and in pathological context such as in Parkinson disease (PD). PD patient derived iPSC generation is in progress (collaboration with Cristina D’Aniello and Teresa Esposito) and iPSC-derived mdA neruons will be generated in order to study the ncRNA involvement in PD pathogenesis.
In collaboration with Emilia Caputo establishing a breast cancer patient derived organoids biobank with the aim to identify points of vulnerability for drug targeting.
The Multifaceted Roles of Proline in Cell Behavior. Patriarca EJ, Cermola F, D’Aniello C, Fico A, Guardiola O, De Cesare D, Minchiotti G. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Aug 12;9:728576.
Interplay between DNA and RNA Modifications: A Constantly Evolving Process. Fico A, Di Croce L, Matarazzo MR. Epigenomes. 2020 Nov 23;4(4):26.
Long Non-coding RNA T-UCstem1 Controls Progenitor Proliferation and Neurogenesis in the Postnatal Mouse Olfactory Bulb through Interaction with miR-9.Pascale E, Beclin C, Fiorenzano A, Andolfi G, Erni A, De Falco S, Minchiotti G, Cremer H, Fico A. Stem Cell Reports. 2020 Oct 13;15(4):836-844. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2020.08.009. Epub 2020 Sep 24.
Long non-coding RNA in stem cell pluripotency and lineage commitment: functions and evolutionary conservation. Fico A, Fiorenzano A, Pascale E, Patriarca EJ, Minchiotti G. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019 Apr;76(8):1459-1471.
LncRNAs and PRC2: Coupled Partners in Embryonic Stem Cells. Fiorenzano A, Pascale E, Patriarca EJ, Minchiotti G, Fico A. Epigenomes. 2019 Aug 6;3(3):14.
An Ultraconserved Element Containing lncRNA Preserves Transcriptional Dynamics and Maintains ESC Self-Renewal. Fiorenzano A, Pascale E, Gagliardi M, Terreri S, Papa M, Andolfi G, Galasso M, Tagliazucchi GM, Taccioli C, Patriarca EJ, Cimmino A, Matarazzo MR, Minchiotti G, Fico A. Stem Cell Reports. 2018 Mar 13;10(3):1102-1114.
Vitamin C and l-Proline Antagonistic Effects Capture Alternative States in the Pluripotency Continuum. D’Aniello C, Habibi E, Cermola F, Paris D, Russo F, Fiorenzano A, Di Napoli G, Melck DJ, Cobellis G, Angelini C, Fico A, Blelloch R, Motta A, Stunnenberg HG, De Cesare D, Patriarca EJ, Minchiotti G. Stem Cell Reports. 2017 Jan 10;8(1):1-10.
Cripto is essential to capture mouse epiblast stem cell and human embryonic stem cell pluripotency. Fiorenzano A, Pascale E, D’Aniello C, Acampora D, Bassalert C, Russo F, Andolfi G, Biffoni M, Francescangeli F, Zeuner A, Angelini C, Chazaud C, Patriarca EJ, Fico A, Minchiotti G. Nat Commun. 2016 Sep 2;7:12589.
c-Myc modulation: a key role in melanoma drug response. Fico A, Alfano D, Valentino A, Vasta V, Cavalcanti E, Travali S, Patriarca EJ, Caputo E. Cancer Biol Ther. 2015;16(9):1375-86.
A novel autoregulatory loop between the Gcn2-Atf4 pathway and l-Proline metabolism controls stem cell identity. D’Aniello C, Fico A, Casalino L, Guardiola O, Di Napoli G, Cermola F, De Cesare D, Tatè R, Cobellis G, Patriarca EJ, Minchiotti G. Cell Death Differ. 2015 Jul;22(7):1234.
Ran signaling in melanoma: implications for the development of alternative therapeutic strategies. Caputo E, Wang E, Valentino A, Crispi S, De Giorgi V, Fico A, Ficili B, Capone M, Anniciello A, Cavalcanti E, Botti G, Mozzillo N, Ascierto PA, Marincola FM, Travali S. Cancer Lett. 2015 Feb 1;357(1):286-296.
Reducing glypican-4 in ES cells improves recovery in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease by increasing the production of dopaminergic neurons and decreasing teratoma formation. Fico A, de Chevigny A, Melon C, Bohic M, Kerkerian-Le Goff L, Maina F, Dono R, Cremer H. J Neurosci. 2014 Jun 11;34(24):8318-23.
The G-protein-coupled receptor APJ is expressed in the second heart field and regulates Cerberus-Baf60c axis in embryonic stem cell cardiomyogenesis. D’Aniello C, Fiorenzano A, Iaconis S, Liguori GL, Andolfi G, Cobellis G, Fico A, Minchiotti G. Cardiovasc Res. 2013 Oct 1;100(1):95-104.
Modulating Glypican4 suppresses tumorigenicity of embryonic stem cells while preserving self-renewal and pluripotency. Fico A, De Chevigny A, Egea J, Bösl MR, Cremer H, Maina F, Dono R. Stem Cells. 2012 Sep;30(9):1863-74.
High-throughput screening-compatible single-step protocol to differentiate embryonic stem cells in neurons. Fico A, Manganelli G, Simeone M, Guido S, Minchiotti G, Filosa S. Stem Cells Dev. 2008 Jun;17(3):573-84.
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase plays a crucial role in protection from redox-stress-induced apoptosis. Fico A, Paglialunga F, Cigliano L, Abrescia P, Verde P, Martini G, Iaccarino I, Filosa S. @Cell Death Differ. 2004 Aug;11(8):823-31.
Current Position
2011 – Research Scientist at IGB-ABT, CNR, Naples, Italy
Research Training
2007-2011 Post-doc at Development Biology Institute of Marseille Luminy, France
2005-2007 Fellow at IGB-ABT, CNR, Naples, Italy
2004-2005 Fellow at University of Naples “Federico II”, Naples, Italy
2000-2004 PhD student at IGB-ABT, CNR, Naples, Italy
1998-2000 Undergraduate student at IGB-ABT, CNR, Naples, Italy
Education
2004 PhD in Genetics, University of Naples “Federico II”, Naples, Italy
1999 B.A. cum laude in Biology, University of Naples “Federico II”, Naples, Italy
Collaborations
Harold Cremer (Aix-Marseille University, CNRS, IBDM, 13288 Marseille, France)
Fanny Mann (Aix-Marseille University, CNRS, IBDM, 13288 Marseille, France)
Silvia Cappello (Max Planck Institute of Psychiatry, 80804 Munich, Germany)
Mariangela Morlando (University of Perugia, 06123 Perugia, Italy)
Emilia Caputo (IGB-ABT, CNR, Naples, Italy)
Teresa Esposito (IGB-ABT, CNR, Naples, Italy)
Memberships in Scientific Societies
2015-present Società Italiana Biofisica e Biologia Molecolare (SIBBM)
2017-present International Society for Stem Cell Research (ISSCR)
Meetings Organization
2018 EMBO Workshop ‘From epigenome towards epitranscriptome in cell fate choice’ Capri, Italy (14-17 October)
2006, 2007 and 2012 Annual Stem Cell Differentiation Training Course, IGB, Naples, Italy
![]() arianna.coppola@igb.cnr.it
arianna.coppola@igb.cnr.it
![]() lorenzo.membrini@igb.cnr.it
lorenzo.membrini@igb.cnr.it