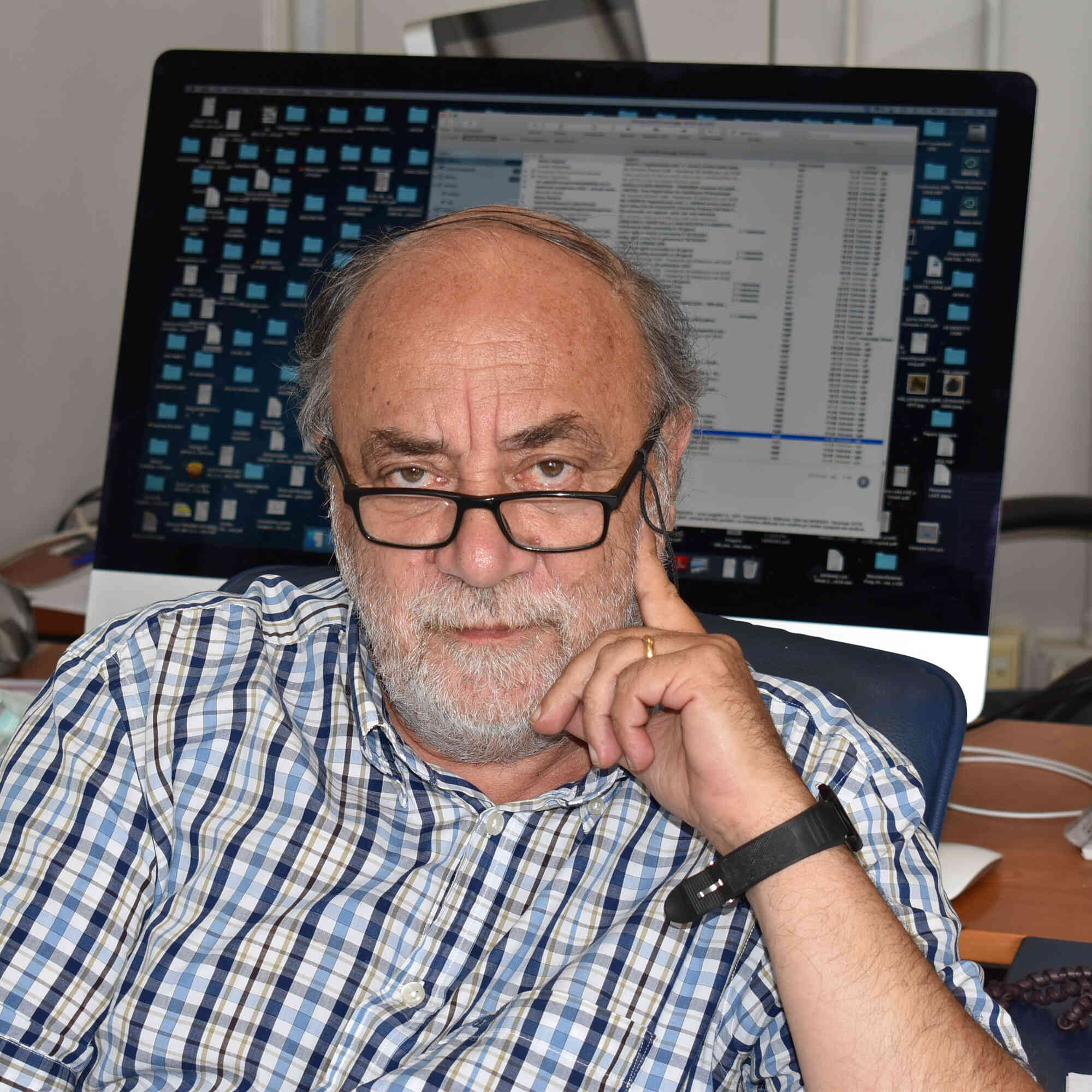
Antonio Simeone
Acting Director
![]() +39 081 6132 242/401
+39 081 6132 242/401 ![]() antonio.simeone@igb.cnr.it
antonio.simeone@igb.cnr.it
Embryonic Development and Biology of Stem Cells – Neurobiology and Brain Functioning
Keywords:
- Research Interest
- Selected Publications
- Professional Experience
- Research Group
1980-1984:
• Role of unequal crossing-over in the evolution of ribosomal genes.
• Molecular and structural organization of the non-transcribed spacer (NTS) of ribosomal DNA of D. melanogaster.
• Identification of transcription and processing signals of ribosomal genes of D. melanogaster.
• Isolation and characterization of alternative messenger RNAs coding class I HLA genes.
1985-1991:
• Isolation and identification of the structural organization of the human homeobox gene family (HOX Complex).
• Expression analysis of several Hox genes in human embryos.
• Expression analysis of the human Hox Complex in teratocarcinoma cells (N-tera2/D1) upon treatment with retinoic acid and the definition of temporal colinearity concept.
• Molecular mechanism controlling the expression of the HOX Complex gene family in human teratocarcinoma cells (N-tera2/D1).
1992-1998:
• Isolation of the murine homologs of the otd and ems homeobox containing genes and analysis of their expression during brain development.
• Isolation and expression analysis both in invertebrate and vertebrate embryos of a new homeobox containing gene named Orthopedia (Otp).
• Isolation and expression analysis in murine embryos of Dlx5 and Dlx6, two murine homologues of the Drosophila Distal-less gene.
• Combined expression analysis of Otx, Emx, Dlx and Otp during development and definition of brain segmentary identities.
• Temporal map during gastrulation of the retinoic acid effect on development and patterning of murine brain.
• Role of Otx2 in the specification of rostral CNS (forebrain, midbrain and anterior hindbrain).
• Role of Otx1 in corticogenesis, pituitary functions and sense organs development.
• Identification of an Otx gene-dosage dependent mechanism required for patterning of developing brain and proper positioning of midbrain-hindbrain isthmic organizer.
• In vivo dissection of Otx1 and Otx2 roles in brain development by using reciprocal knock-in mouse models: definition of extended functional equivalence between OTX1 and OTX2 proteins and the relevance of the Otx1 and Otx2 differential transcriptional control.
1999-2005:
• Dissection of Otx2 roles during gastrulation: requirement of Otx2 in the visceral endoderm for specification of anterior identity, and in the early neuroectoderm for maintenance of the anterior identity (forebrain and midbrain).
• Role of Otx1 and Otx2 in brain evolution: functional equivalence between the invertebrate Orthodenticle and the murine OTX1 and OTX2 gene products supports a conserved genetic program of brain development between insects and mammals.
• Role of Orthopedia (Otp) in proliferation, migration and differentiation of the murine neuroendocrine hypothalamus.
• Differential dosage-dependent roles of OTX2 in specifying regional identities and neuronal cell types during brain development.
• Antagonistic role of Otx2 and Gbx2 in regionalization of midbrain and rostral hindbrain.
• Evidence for an Otx2-dependent control of dorso-ventral patterning of the midbrain.
• Role of Otx2 in the control of identity and fate of neuronal precursors in the ventral midbrain.
2006-2012
• Otx2 cell-autonomous control of thalamic glutamatergic progenitors.
• Expression complexity of the Otx2 locus: transcriptional, post-transcriptional and translational regulation of Otx2 mRNA isoforms control specification and maintenance of forebrain and midbrain regional identities.
• Role of Otx2 in dopaminergic neurogenesis: dose-dependent, anterior -posterior and dorsal-ventral integrated control by Otx2 regulates proliferation, number and neurotransmitter phenotype of dopaminergic progenitors.
• Role of Otx2 in adult dopaminergic neurons: Otx2 specify post-mitotic neuron subtype identity in ventral tegmental area (VTA) and antagonizes dopaminergic vulnerability to the Parkinsonian neurotoxin MPTP.
• Role of Orthopedia in neurogenesis of diencephalic dopaminergic neurons.
• Role of Orthopedia in migration of diencephalic progenitors fated to populate the telencephalic amygdala.
• Role of Otx1 and Otx2 in initiation and progression of desmoplastic Sonic Hedgehog-dependent medulloblastomas.
• Identification of Otx1 as a selective diagnostic marker of aggressive Lymphomas.
2013 up today
• Role of Otx2 in neurogenesis and regional identity of dorsal midbrain.
• Role of Otx2 in Embryonic Stem Cells (ESCs): Otx2 is an intrinsic determinant required to maintain the ESC metastable state by antagonizing ground state pluripotency and promoting commitment to differentiation.
• Role of Otx2 in Epiblast Stem Cells (EpiSCs): Otx2 stabilizes the primed EpiSC state by suppressing mesendoderm into neural fate switch in cooperation with BMP4 and Fgf2.
• Role of Otx2 in ESC-based induction of telencephalic neurons: Otx2- mediated requirement for specification of dorsal cortical neurons.
• Role of Otx2 in the transition to primed pluripotency: Otx2 controls transition into primed pluripotency by recruiting Oct4 at new enhancers associated to ESC-derived epiblast-like cells (EpiLCs) differentiation.
• Design of a diagnostic kit to predict late onset of sporadic Parkinson’s Disease.
• Role of Otx2 in the direct control of the Nanog pluripotency core factor: through binding to the Nanog promoter, Otx2 controls the integrity of specific ESC sub-type compartments and in vivo the differentiation of the the epiblast lineage.
• Role of Otx2 in metastability: through mutual antagonism, Otx2 and Nanog specify the heterogeneous identity of metastable ESCs and individually predispose ESCs for optimal response to naïve or formative inducing factors.
Hirsch (H) Index and list of Publications (Research Articles and Reviews)
H Index Google Scholar: 80 Citations: 20246
H-index ISI Web: 71 Citations: 14467
H-index Scopus: 70 Citations: 14190
170) A. Gialluisi, M. G. Reccia, N. Modugno, T. Nutile, A. Lombardi, L. G. Di Giovannantonio, S. Pietracupa, D. Ruggiero, S. Scala, S. Gambardella, International Parkinson’s Disease Genomics Consortium (IPDGC), L Iacoviello, F. Gianfrancesco, D. Acampora, M. D’Esposito, A. Simeone, M. Ciullo and T. Esposito. Identification of sixteen novel candidate genes for late onset Parkinson’s disease. Molecular Neurodegeneration, 16:35 (2021), doi.org/10.1186/s13024-021-00455-2
169) L. G. Di Giovannantonio, D. Acampora, D. Omodei, V. Nigro, P. Barba, E. Barbieri, I. Chambers, A. Simeone. Direct repression of Nanog and Oct4 by OTX2 modulates the contribution of epiblast-derived cells to germline and somatic lineage. Development 148 (2021), dev199166. doi:10.1242/dev.19916
168) Gialluisi, A., Reccia, M.G., Tirozzi, A., Nutile, T., Lombardi, A., De Sanctis, C., Varanese, S.,Pietracupa, S., Modugno, N., Simeone, A., Ciullo, M., Esposito, T., International Parkinson’s DiseaseGenomic Consortium (IPDGC). Whole Exome Sequencing Study of Parkinson Disease and Related Endophenotypes in the Italian Population. Frontiers in Neurology 2020. 10(1362)
167) Imbriglio T, Verhaeghe R, Martinello K, Pascarelli MT, Chece G, Bucci D, Notartomaso S, Quattromani M, Mascio G, Scalabrì F, Simeone A, Maccari S, Del Percio C, Wieloch T, Fucile S, Babiloni C, Battaglia G, Limatola C, Nicoletti F, Cannella M. Developmental abnormalities in cortical GABAergic system in mice lacking mGlu3 metabotropic glutamate receptors. FASEB J. 2019 33, 14204-14220
166) Rosati J, Ferrari D, Altieri F, Tardivo S, Ricciolini C, Fusilli C, Zalfa C, Profico DC, Pinos F, Bernardini L, Torres B, Manni I, Piaggio G, Binda E, Copetti M, Lamorte G, Mazza T, Carella M, Gelati M, Valente EM, Simeone A, Vescovi AL. Establishment of stable iPS-derived human neural stem cell lines suitable for cell therapies. Cell Death Dis. 9, 937 (2018)
165) J. Zhang, M. Zhang, D. Acampora, D. Yuan, A. Simeone, I. Chambers. Otx2 restricts entry to the mouse germline. Nature 562, 595-599 (2018)
164) D. Acampora, L. G. Di Giovannantonio, A. Garofalo, V. Nigro, D. Omodei, A. Lombardi, J. Zhang, I. Chambers & A. Simeone. Functional antagonism between OTX2 and NANOG specifies a spectrum of heterogeneous identities in embryonic stem cells. Stem Cell Reports. 9, 1642-1659 (2017)
163) H. H. Lee, C. Bernard, Z. Ye, D. Acampora, A. Simeone, A. Prochiantz, A. A. Di Nardo & T. K. Hensch. Genetic Otx2 mis-localization delays critical period plasticity across brain regions. Mol. Psychiatry 22, 680-688 (2017)
162) D. Acampora, D. Omodei, G. Petrosino, A. Garofalo, M. Savarese, V. Nigro, L. G. Di Giovannantonio, V. Mercadante & A. Simeone. Loss of Otx2 binding site to the Nanog promoter affects integrity of embryonic stem cell sub-type compartments and differentiation of inner cell mass-derived epiblast. Cell Reports 15, 2651-64 (2016)
161) H. T. Kim, S. J. Kim, Y. I. Sohn, S. S. Paik, R. Caplette, M. Simonutti, K. H. Moon, E. J. Lee, K. W. Min, M. J. Kim, D. G. Lee, A. Simeone, T. Lamonerie, T. Furukawa, J. S. Choi, H. S. Kweon, S. Picaud, I. B. Kim, M. Shong & J. W. Kim. Mitochondrial Protection by Exogenous Otx2 in Mouse Retinal Neurons. Cell Reports 13, 990-1002 (2015)
160) Y. Fukusumi, F. Meier, S. Götz, F. Matheus, M. Irmler, R. Beckervordersandforth, T. Faus-Kessler, E. Minina, B. Rauser, J. Zhang, E. Arenas, E. Andersson, C. Niehrs, J. Beckers, A. Simeone, W. Wurst & N. Prakash. Dickkopf 3 Promotes the Differentiation of a Rostrolateral Midbrain Dopaminergic Neuronal Subset In Vivo and from Pluripotent Stem Cells In Vitro in the Mouse. J Neurosci. 35,13385-401 (2015)
159) J. Zhang, S. Götz, D. M. Vogt Weisenhorn, A. Simeone, W. Wurst, & N. Prakash. A WNT1-regulated developmental gene cascade prevents dopaminergic neurodegeneration in adult En1(+/-) mice. Neurobiol Dis. 82, 32-45. (2015)
158) N. Kim, D. Acampora, F. Dingli, D. Loew, A. Simeone, A. Prochiantz & A. Di Nardo. Immunoprecipitation and mass spectrometry identify non-cell autonomous Otx2 homeoprotein in the granular and supragranular layers of mouse visual cortex. F1000 Res. 3,178 (2014)
157) L. Panman, M. Papathanou, A. Laguna, T. Oosterveen, N. Volakakis, D. Acampora, I. Kurtsdotter, T. Yoshitake, J. Kehr, E. Joodmardi, J. Muhr, A. Simeone, J. Ericson & T. Perlmann. Sox6 and Otx2 control the specification of substantia nigra and ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons. Cell Reports 8,1018-1025 (2014)
156) F. Meier, F. Giesert, S. Delic, T. Faus-Kessler, F. Matheus, A. Simeone, S. M. Hölter, R. Kühn, D. M. Weisenhorn, W. Wurst & N. Prakash. FGF/FGFR2 signaling regulates the generation and correct positioning of Bergmann glia cells in the developing mouse cerebellum. PLoS One. 9:e101124 (2014)
155) C. Buecker, R. Srinivasan, Z. Wu, E. Calo, D. Acampora, T. Faial, A. Simeone, M. Tan, T. Swigut & J. Wysocka. Reorganization of enhancer patterns in transition from naïve to primed pluripotency. Cell Stem Cell. 14, 838-853 (2014)
154) Y. Bozzi & A. Simeone. Otx genes and seizure susceptibility. Molecular & Cellular Epilepsy, vol 1, n. 3, doi: 10.14800/mce.74 (2014)
153) PP. Tripathi, LG. Di Giovannantonio, E. Sanguinetti, D. Acampora, M. Allegra, M. Caleo, W. Wurst, A. Simeone & Y. Bozzi. Increased dopaminergic innervation in the brain of conditional mutant mice overexpressing Otx2: Effects on locomotor behavior and seizure susceptibility. Neuroscience 261,173-183 (2014)
152) L.G. Di Giovannantonio, M. Di Salvio, D. Omodei, N. Prakash, W. Wurst, A. Pierani, D. Acampora & A. Simeone. Otx2 cell-autonomously determines dorsal mesencephalon versus cerebellum fate independently of isthmic organizing activity. Development. 14, 1377-1388 (2014)
151) C. Bernard, H.T. Kim, Ibad R. Torero, E.J. Lee, M. Simonutti, S. Picaud, D. Acampora, A. Simeone, A.A. Di Nardo, A. Prochiantz, K.L. Moya & J.W. Kim. Graded Otx2 activities demonstrate dose-sensitive eye and retina phenotypes. Hum Mol Genet. 23,1742-1753 (2014)
150) H. Meziane, V. Fraulob, F. Riet, W. Krezel, M. Selloum, M. Geffarth, D. Acampora, Y. Hérault, A. Simeone, M. Brand, P. Dollé & M. Rhinn. The homeodomain factor Gbx1 is required for locomotion and cell specification in the dorsal spinal cord. Peer J. 1:e142 (2013)
149) P. A. Johansson, M. Irmler, D. Acampora, J. Beckers, A. Simeone & M. Götz. The transcription factor Otx2 regulates choroid plexus development and function. Development. 140, 1055-66 (2013)
148) L. G. Di Giovannantonio, M. Di Salvio, D. Acampora, N. Prakash, W. Wurst & A. Simeone. Otx2 selectively controls the neurogenesis of specific neuronal subtypes of the ventral tegmental area and compensates En1-dependent neuronal loss and MPTP vulnerability. Dev. Biol. 373, 176-183 (2013)
147) D. Acampora, L. G. Di Giovannantonio & A. Simeone. Otx2 is an intrinsic determinant of the Embryonic Stem Cell state and is required for transition to a stable Epiblast Stem Cell condition. Development. 140, 43-55 (2013)
146) T. Valentino, D. Palmieri, M. Vitiello, A. Simeone, G. Palma, C. Arra, P. Chieffi, L. Chiariotti, A. Fusco & M. Fedele. Embryonic defects and growth alteration in mice with homozygous disruption of the Patz1 gene. J. Cell Physiol. 228, 646-53 (2013)
145) T. Burgold, N. Voituron, M. Caganova, P. P. Tripathi, C. Menuet, B. K. Tusi, F. Spreafico, M. Bèvengut, C. Gestreau, S. Buontempo, A. Simeone, L. Kruidenier, G. Natoli, S. Casola, G. Hilaire & G. Testa. The H3K27 Demethylase JMJD3 Is Required for Maintenance of the Embryonic Respiratory Neuronal Network, Neonatal Breathing, and Survival. Cell Reports 2, 1244-1258 (2012)
144) M. Y. Turco, L. Furia, A. Dietze, L. Fernandez Diaz, S. Ronzoni, A. Sciullo, A. Simeone, D. Constam, M. Faretta & L. Lanfrancone. Cellular Heterogeneity During Embryonic Stem Cell Differentiation to Epiblast Stem Cells is Revealed by the ShcD/RaLP Adaptor Protein. Stem Cells. 30, 2423-36 (2012)
143) A. Simeone, E. Puelles, D. Omodei, D. Acampora, L. G. Di Giovannantonio, M. Di Salvio, P. Mancuso & C. Tomasetti. Otx genes in neurogenesis of mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons. Dev. Neurobiol. 71, 665-679 (2011)
142) T. Fischer, T. Faus-Kessler, G. Welzl, A. Simeone, W. Wurst & N. Prakash. Fgf15-mediated control of neurogenic and proneural gene expression regulates dorsal midbrain neurogenesis. Dev. Biol. 350, 496-510 (2011)
141) A. Simeone, M. Di Salvio, L. G. Di Giovannantonio, D. Acampora, D. Omodei & C. Tomasetti. The Role of Otx2 in Adult Mesencephalic-Diencephalic Dopaminergic Neurons. Mol. Neurobiol. 43, 107-113 (2011)
140) M. Di Salvio, L. G. Di Giovannantonio, D. Acampora, R. Prosperi, D. Omodei, N. Prakash, W. Wurst & A. Simeone. Otx2 controls neuron subtype identity in ventral tegmental area and antagonizes vulnerability to MPTP. Nature Neurosci. 13, 1481-1488 (2010)
139) H. Tilleman, V. Hakim, O. Novikov, K. Liser, L. Nashelsky, M. Di Salvio, M. Krauthammer, O. Scheffner, I. Maor, O. Mayseless, I. Meir, G. Kayam, D. Sela-Donenfeld, A. Simeone & C. Brodski. Bmp5/7 in concert with the mid-hindbrain organizer control development of noradrenergic locus coeruleus neurons. Mol Cell Neurosci. 45, 1-11 (2010)
138) F. García-Moreno, M. Pedraza, L. G. Di Giovannantonio, M. Di Salvio, L. López-Mascaraque, A. Simeone & J.A. De Carlos. A neuronal migratory pathway crossing from diencephalon to telencephalon populates amygdala nuclei. Nature Neurosci.13, 680-689 (2010)
137) C. Y. Chung, P. Licznerski, K.N. Alavian, A. Simeone, Z. Lin, E. Martin, J. Vance & O. Isacson. The transcription factor orthodenticle homeobox 2 influences axonal projections and vulnerability of midbrain dopaminergic neurons. Brain. 133, 2022-2031 (2010)
136) M. Di Salvio, L. G. Di Giovannantonio, D. Omodei, D. Acampora & A. Simeone. Otx2 expression is restricted to dopaminergic neurons of the ventral tegmental area in the adult brain. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 54, 939-945 (2010)
135) A. Simeone, E. Puelles, D. Acampora, D. Omodei, P. Mancuso & L. G. Di Giovannantonio. The role of Otx genes in progenitor domains of ventral midbrain. Adv Exp Med Biol. 651, 36-46 (2009)
134) N. Prakash, E. Puelles, K. Freude, D. Trümbach, D. Omodei, M. Di Salvio, L. Sussel, J. Ericson, M. Sander, A. Simeone* & W. Wurst. Nkx6-1 controls the identity and fate of red nucleus and oculomotor neurons in the mouse midbrain. Development 136, 2545-2555 (2009)
133) D. Omodei, D. Acampora, F. Russo, R. De Filippi, V. Severino, R. Di Francia, F. Frigeri, P. Mancuso, A. De Chiara, A. Pinto, S. Casola & A. Simeone. Expression of the brain transcription factor OTX1 occurs in a subset of normal germinal-center B cells and in aggressive Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Am. J. Pathol. 175, 2609-2617 (2009)
132) C. H. Hwang, A. Simeone, E. Lai & D. K. Wu. Foxg1 is required for proper separation and formation of sensory cristae during inner ear development. Dev. Dyn. 238, 2725-2734 (2009)
131) D. Acampora, L. G. Di Giovannantonio, M. Di Salvio, P. Mancuso & A. Simeone. Selective inactivation of Otx2 mRNA isoforms reveals isoform-specific requirement for visceral endoderm anteriorization and head morphogenesis and highlights cell diversity in the visceral endoderm. Mech. Dev. 126, 882-897 (2009)
130) P. P. Tripathi, L. G. Di Giovannantonio, A. Viegi, W. Wurst, A. Simeone* & Y. Bozzi. Serotonin Hyperinnervation Abolishes Seizure Susceptibility in Otx2 Conditional Mutant Mice. The Journal of Neuroscience 28, 9271-9276 (2008)
129) D. Omodei, D. Acampora, P. Mancuso, N. Prakash, L. G. Di Giovannantonio, W. Wurst & A. Simeone. Anterior-posterior graded response to Otx2 controls proliferation and differentiation of dopaminergic progenitors in the ventral mesencephalon. Development 135, 3459-3470 (2008)
128) T. Heimbucher, C. Murko, B. Bajoghli, N. Aghaallaei, A. Huber, R. Stebegg, D. Eberhard, M. Fink, A. Simeone & T. Czerny. Gbx2 and Otx2 interact with the WD40 domain of Groucho/Tle corepressors. Mol Cell Biol. 27, 340-51 (2007)
127) S. Ryu, J. Mahler, D. Acampora, J. Holzschuh, S. Erhardt, D. Omodei, A. Simeone* & W. Driever. Orthopedia homeodomain protein is essential for diencephalic dopaminergic neuron development. Current Biology 17, 873-80 (2007)
126) A. Borgkvist, E. Puelles, M. Carta, D. Acampora, S. L. Ang, W. Wurst, M. Goiny, G. Fisone, A. Simeone* & A. Usiello. Altered dopaminergic innervation and amphetamine response in adult Otx2 conditional mutant mice. Mol Cell Neurosci. 31, 293-302 (2006)
125) N. Prakash, C. Brodski, T. Naserke, E. Puelles, R. Gogoi, A. Hall, M. Panhuysen, D. Echevarria, L. Sussel, D. M. Weisenhorn, S. Martinez, E. Arenas, A. Simeone* & W. Wurst. A Wnt1-regulated genetic network controls the identity and fate of midbrain-dopaminergic progenitors in vivo. Development. 133, 89-98 (2006)
124) G. Griesel, D. Treichel, P. Collombat, J. Krull, A. Zembrzycki, W. M. van den Akker, P. Gruss, A. Simeone & A. Mansouri. Sp8 controls the anteroposterior patterning at the midbrain-hindbrain border. Development. 133, 1779-87 (2006)
123) I. Foucher, M. Mione, A. Simeone, D. Acampora, L. Bally-Cuif & C. Houart. Differentiation of cerebellar cell identities in absence of Fgf signalling in zebrafish Otx morphants. Development. 133, 1891-900 (2006)
122) E. Puelles, D. Acampora, R. Gogoi, F. Tuorto, A. Papalia, F. Guillemot, S. L. Ang & A. Simeone. Otx2 controls identity and fate of glutamatergic progenitors of the thalamus by repressing GABAergic differentiation. The Journal of Neuroscience 26, 5955-64 (2006)
121) A. Simeone. The genetic control of dopaminergic differentiation. Trends Neurosci. 28, 62-65 (2005)
120) B. Vernay, M. Koch, F. Vaccarino, J. Briscoe, A. Simeone, R. Kageyama & S. L. Ang. Otx2 regulates subtype specification and neurogenesis in the midbrain. The Journal of Neuroscience 25, 4856-4867 (2005)
119) D. Acampora, A. Annino, F. Tuorto, E. Puelles, W. Lucchesi, A. Papalia & A. Simeone. Otx genes in the evolution of the vertebrate brain. Brain Res Bull. 15, 410-420 (2005)
118) M. Rhinn, K. Lun, M. Werner, A. Simeone & M. Brand. Isolation and expression of the homeobox gene Gbx1 during mouse development. Developmental Dynamics 229, 334-339 (2004)
117) D. M. Shin, S. Korada, R. Raballo, C. S. Shashikant, A. Simeone, J. R. Taylor & F. Vaccarino. Loss of glutamatergic pyramidal neurons in frontal and temporal cortex resulting from attenuation of FGFR1 signaling is associated with spontaneous hyperactivity in mice. The Journal of Neuroscience 24, 2247-2258 (2004)
116) E. Puelles, A. Annino, F. Tuorto, A. Usiello, D. Acampora, T. Czerny, S. L. Ang, W. Wurst & A. Simeone. Otx2 regulates the extent, identity and fate of neuronal progenitor domains in the ventral midbrain. Development 131, 2037-2048 (2004)
115) C. Brodski, D. M. Vogt Weisenhorn, M. Signore, I. Sillaber, M. Oesterheld, V. Broccoli, D. Acampora, A. Simeone* & W. Wurst. Location and size of dopaminergic and serotonergic cell populations are controlled by the position of the midbrain-hindbrain organizer. The Journal of Neuroscience 23, 4199-4207 (2003)
114) E. Puelles, D. Acampora, E. Lacroix, M. Signore, A. Annino, F. Tuorto, S. Filosa, G. Corte, W. Wurst, S. L. Ang & A. Simeone. Otx dose-dependent integrated control of antero-posterior and dorso-ventral patterning of midbrain. Nature Neuroscience 6, 453-460 (2003)
113) D. Acampora, A. Annino, E. Puelles, I. Alfano, F. Tuorto & A. Simeone. OTX1 compensates for OTX2 requirement in regionalisation of anterior neuroectoderm. Gene expr. Patterns 3, 497-501 (2003)
112) E. Levantini, A. Giorgetti, F. Cerisoli, E. Traggiai, A. Guidi, R. Martin, D. Acampora, P. D. Aplan, G. Keller, A. Simeone, N. N. Iscove, T. Hoang & M. C. Magli. Unsuspected role of the brain morphogenetic gene Otx1 in hematopoiesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100, 10299-10303 (2003)
111) J. P. Barbera, T. A. Rodriguez, N. D. Greene, W. J. Weninger, A. Simeone, A. J. Copp, R. S. Beddington & S. Dunwoodie. Folic acid prevents exencephaly in Cited2 deficient mice. Hum Mol Genet 11, 283-293 (2002).
110) H. Montalta-He, R. Leemans, T. Loop, M. Strahm, U. Certa, M. Primig, D. Acampora, A. Simeone & H. Reichert. Evolutionary conservation of otd/Otx2 transcription factor action: a genome-wide microarray analysis in Drosophila. Genome Biol 3, RESEARCH0015 (2002).
109) R. Gogoi, F. Schubert, J. Martinez-Barbera, D. Acampora, A. Simeone & A. Lumsden. The paired-type homeobox gene Dmbx1 marks the midbrain and pretectum. Mechanisms of Development 114, 213 (2002)
108) A. Simeone. Towards the comprehension of genetic mechanisms controlling brain morphogenesis. Trends in Neurosciences 25, 119-121 (2002)
107) A. Simeone, E. Puelles & D. Acampora. The Otx family. Curr Opin Genet Dev 12, 409-415 (2002)
106) B. Cipelletti, G. Avanzini, L. Vitellaro-Zuccarello, S. Franceschetti, G. Sancini, T. Lavazza, D. Acampora, A. Simeone, R. Spreafico & C. Frassoni. Morphological organization of somatosensory cortex in Otx1(-/-) mice. Neuroscience 115, 657-67 (2002).
105) J. R. Martinez Morales, M. Signore, D. Acampora, A. Simeone & P. Bovolenta. Otx genes are required for tissue specification in the developing eye. Development 128, 2019-2030 (2001)
104) P. Pilo Boyl, M. Signore, D. Acampora, J. P. Martinez-Barbera, C. Ilengo, A. Annino, G. Corte & A. Simeone. Forebrain and midbrain development requires epiblast-restricted Otx2 translational control mediated by its 3’ UTR. Development 128, 2989-3000 (2001)
103) J. P. Martinez-Barbera, M. Signore, P. Pilo Boyl, E. Puelles, D. Acampora, R. Gogoi, F. Schubert, A. Lumsden & A. Simeone. Regionalisation of anterior neuroectoderm and its competence in responding to forebrain and midbrain inducing activities depend on mutual antagonism between OTX2 and GBX2. Development 128, 4789-4800 (2001)
102) D. Acampora, P. Pilo Boyl, M. Signore, J. P. Martinez-Barbera, C. Ilengo, E. Puelles, A. Annino, H. Reichert, G. Corte & A. Simeone. OTD/OTX2 functional equivalence depends on 5’ and 3’ UTR-mediated control of Otx2 mRNA for nucleo-cytoplasmic export and epiblast-restricted translation. Development 128, 4801-4813 (2001)
101) A. Simeone & D. Acampora. The role of Otx2 in organizing the anterior patterning in mouse. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 45: 337-345 (2001)
100) D. Acampora, M. Gulisano, V. Broccoli & A. Simeone. Otx genes in brain morphogenesis. Progress in Neurobiology 64, 69-95 (2001)
99) P. Pilo Boyl, M. Signore, A. Annino, J. P. Martinez Barbera, D. Acampora & A. Simeone. Otx genes in the development and evolution of the vertebrate brain. Int. J. Dev. N. 19, 353-363 (2001)
98) D. Acampora, P. Pilo Boyl, J. P. Martinez Barbera, A. Annino, M. Signore & A. Simeone. Otx genes in evolution: are they involved in instructing the vertebrate brain morphology? Journal of Anatomy 199, 53-62 (2001)
97) H. Reichert & A. Simeone. Developmental genetic evidence for a monophyletic origin of the bilaterian brain. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 356,1 533-544 (2001)
96) B. Fritzsch, M. Signore & A. Simeone. Otx1 null mutant mice show partial segregation of sensory epithelia comparable to lamprey ears. Development, Genes & Evolution 211, 388-396 (2001)
95) A. Simeone. Positioning the isthmic organizer where Otx2 and Gbx2 meet. Trends in Genetics 16, 237-240 (2000)
94) D. Acampora, M. Gulisano & A. Simeone. Genetic and molecular roles of Otx homeodomain proteins in head development. Gene 246, 23-35 (2000)
93) D. Acampora, M. P. Postiglione, V. Avantaggiato, M. Di Bonito & A. Simeone. The role of Otx and Otp genes in brain development. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 44, 669-677 (2000)
92) N. Offenhäuser, E. Santolini, A. Simeone & P. P. Di Fiore. Differential patterns of expression of Eps15 and Eps15R during mouse embryogenesis. Mechanisms of Development 95, 309-312 (2000)
91) R. Cantos, L. K. Cole, D. Acampora, A. Simeone & D. K. Wu. Patterning of the mammalian cochlea. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 97, 11707-11713 (2000)
90) G. Avanzini, R. Spreafico, B. Cipelletti, G. Sancini, C. Frassoni, S. Franceschetti, T. Lavazza, F. Panzica, D. Acampora & A. Simeone. Synaptic properties of neocortical neurons in epileptic mice lacking the Otx1 gene. Epilepsia. 41 Suppl 6, S200-S205 (2000)
89) D. Acampora, M. Gulisano & A. Simeone. Otx genes and the genetic control of brain morphogenesis. Molecular and Cellular Neuroscience 13, 1-8 (1999)
88) M. Hidalgo-Sanchez, S. Millet, A. Simeone & R. M. Alvarado-Mallart. Comparative analysis of Otx2, Gbx2, Pax2, Fgf8 and Wnt1 gene expressions during the formation of the chick midbrain/hindbrain domain. Mechanisms of Development 81, 175-178 (1999)
87) D. Acampora & A. Simeone. Understanding the roles of Otx1 and Otx2 in the control of brain morphogenesis. Trends in Neuroscience 22, 116-122 (1999)
86) D. Acampora, P. Barone & A. Simeone. Otx genes in corticogenesis and brain development. Cerebral Cortex 9, 533-542 (1999)
85) H. Reichert & A. Simeone. Conserved usage of gap and homeotic genes in patterning the CNS. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 9, 589-595 (1999)
84) D. Acampora, V. Avantaggiato, F. Tuorto, P. Barone, M. Perera, G. Corte, & A. Simeone. Differential transcriptional control as the major molecular event in generating Otx1-/- and Otx2-/- divergent phenotypes. Development 126, 1417-1426 (1999)
83) H. Morsli, F. Tuorto, D. Choo, M. P. Postiglione, A. Simeone & D. K. Wu. Otx1 and Otx2 activities are required for the normal development of the mouse inner ear. Development 126, 2335-2343 (1999)
82) M. Hidalgo-Sanchez, A. Simeone & R. M. Alvarado-Mallart. Fgf8 and Gbx2 induction concomitant with Otx2 repression is correlated with midbrain-hindbrain fate of caudal prosencephalon. Development 126, 3191-3203 (1999)
81) D. Acampora, G. Merlo, L. Paleari, B. Zerega, M. P. Postiglione, S. Mantero, E. Bober, O. Barbieri, A. Simeone & G. Levi. Craniofacial, vestibular and bone defects in mice lacking the Distal-less related gene Dlx5. Development 126, 3795-3809 (1999)
80) D. Acampora, M. P. Postiglione, V. Avantaggiato, M. Di Bonito, F. Vaccarino, J. Michaud & A. Simeone. Progressive impairment of developing neuroendocrine cell lineages in the hypothalamus of mice lacking the Orthopedia gene. Genes & Development 13, 2787-800 (1999)
79) D. Acampora, S. Mazan, F. Tuorto, V. Avantaggiato, J. J. Tremblay, D. Lazzaro, A. di Carlo, A. Mariano, P. E. Macchia, G. Corte, V. Macchia, J. Drouin, P. Brûlet & A. Simeone. Transient dwarfism and hypogonadism in mice lacking Otx1 reveal prepubescent stage-specific control of pituitary levels of GH, FSH and LH. Development 125, 1229-1239 (1998)
78) P. Fumagalli, M. Accarino, A. Egeo, P. Scartezzini, G. Rappazzo, A. Pizzuti, V. Avantaggiato, A. Simeone, G. Arrigo, O. Zuffardi, S. Ottolenghi & R. Taramelli. Human NRD convertase: a highly conserved metalloendopeptidase expressed at specific sites during development and in adult tissues. Genomics 47, 238-245 (1998)
77) L. Chiariotti, G. Benvenuto, M. Fedele, M. Santoro, A. Simeone, A. Fusco & C. B. Bruni. Identification and characterization of a novel RING-finger gene (RNF4) mapping at 4p16.3. Genomics 47, 258-265 (1998)
76) A. Simeone. Otx1 and Otx2 in the development and evolution of the mammalian brain. EMBO J. 17, 6790-6798 (1998)
75) T. Nagao, S. Leuzinger, D. Acampora, A. Simeone, R. Finkelstein, H. Reichert & K. Furukubo-Tokunaga. Developmental rescue of Drosophila cephalic defects by the human Otx genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 95, 3737-3742 (1998)
74) D. Acampora, V. Avantaggiato, F. Tuorto, P. Barone, H. Reichert, R. Finkelstein & A. Simeone. Murine Otx1 and Drosophila otd genes share conserved genetic functions required in invertebrate and vertebrate brain development. Development 125, 1691-1702 (1998)
73) S. Leuzinger, F. Hirth, D. Gehrlich, D. Acampora, A. Simeone, W. J. Gehring, R. Finkelstein, K. Furukubo-Tokunaga & H. Reichert. Equivalence of the fly orthodenticle gene and the human OTX genes in embryonic brain development of Drosophila. Development 125, 1703-1710 (1998)
72) P. Buanne, B. Incerti, D. Guardavaccaro, V. Avantaggiato, A. Simeone & F. Tirone. Cloning of the human interferon-related developmental regulator (IFRD1) gene coding for the PC4 protein, a member of a novel family of developmentally regulated genes. Genomics 51, 233-242 (1998)
71) V. Avantaggiato, M. Orlandini, D. Acampora, S. Oliviero & A. Simeone. Embryonic expression pattern of the murine figf gene, a growth factor belonging to platelet-derived growth factor/vascular endothelial growth factor family. Mechanisms of Development 73, 221- 224 (1998)
70) D. Acampora, V. Avantaggiato, F. Tuorto, P. Briata, G. Corte & A. Simeone. Visceral endoderm-restricted translation of Otx1 mediates recovery of Otx2 requirements for specification of anterior neural plate and normal gastrulation. Development 125, 5091-5104 (1998)
69) S. Casarosa, M. Andreazzoli, A. Simeone & G. Barsacchi. Xrx1, a novel Xenopus homeobox gene expressed during eye and pineal gland development. Mechanisms of Development 61, 187-198 (1997)
68) M. Zannini, E. Biffali, M. I. Arnone, K. Sato, M. Pischetola, B. Taylor, S. J. Philips, V. Avantaggiato, A. Simeone & R. Di Lauro. TTF-2, a new forkhead protein, shows a temporal expression in the developing thyroid which is consistent with a role in controlling the onset of differentiation. EMBO J. 16, 3185-3197 (1997)
67) D. Acampora, V. Avantaggiato, F. Tuorto & A. Simeone. Genetic control of brain morphogenesis through Otx gene dosage requirement. Development 127, 3639-3650 (1997)
66) S. Brunelli, A. Faiella, V. Capra, V. Nigro, A. Simeone, A. Cama & E. Boncinelli. Germline mutations in the homeobox gene EMX2 in patients with severe schizencephaly. Nature Genetics 12, 94-96 (1996)
65) V. Avantaggiato, D. Acampora, F. Tuorto & A. Simeone. Retinoic acid induces stage-specific repatterning of the rostral central nervous system. Developmental Biology 175, 347-357 (1996)
64) D. Acampora, S. Mazan, V. Avantaggiato, P. Barone, F. Tuorto, Y. Lallemand, P. Brûlet & A. Simeone. Epilepsy and brain abnormalities in mice lacking Otx1 gene. Nature Genetics 14, 218-222 (1996)
63) S. Millet, E. Bloch-Gallego, A. Simeone & R.M. Alvarado-Mallart. The caudal limit of Otx2 gene expression as a marker of the midbrain/hindbrain boundary: a study using in situ hybridisation and chick/quail homotopic grafts. Development 122, 3785-3797 (1996)
62) M. Pellegrini, A. Mansouri, A. Simeone, E. Boncinelli & P. Gruss. Dentate gyrus formation requires Emx2. Development 122, 3893-3898 (1996)
61) F. Maina, F. Casagranda, E. Audero, A. Simeone, P. M. Comoglio, R. Klein & C. Ponzetto. Uncoupling of Grb2 from the met receptor in vivo reveals complex roles in muscle development. Cell 87, 531-542 (1996)
60) G. Chiappetta, V. Avantaggiato, R. Visconti, M. Fedele, S. Battista, F. Trapasso, B. M. Merciai, V. Fidanza, V. Giancotti, M. Santoro, A. Simeone & A. Fusco. High Level expression of the HMGI (Y) gene during embryonic development. Oncogene 13, 2439-2446 (1996)
59) L. De Gregorio, G. Manenti, A. Simeone & T. A. Dragani. Genetic mapping of the homeobox-containing Otx1 gene on mouse Chromosome 11. Mammalian Genome 7, 241 (1996)
58) A. Simeone, V. Avantaggiato, M. C. Moroni, F. Mavilio, C. Arra, F. Cotelli, V. Nigro & D. Acampora. Retinoic acid induces stage-specific antero-posterior transformation of rostral central nervous system. Mechanisms of Development 51, 83-98 (1995)
57) V. Avantaggiato, P. P. Pandolfi, M. Ruthardt, N. Hawe, D. Acampora, P. G. Pelicci & A. Simeone. Developmental analysis of murine Promyelocyte Leukemia Zinc Finger (PLZF) gene expression: implications for the neuromeric model of the forebrain organization. The Journal of Neuroscience 15, 4927-4942 (1995)
56) A. Simeone, A. Daga & F. Calabi. Expression of runt in the mouse embryo. Developmental Dynamics 203, 61-70 (1995)
55) D. Acampora, S. Mazan, Y. Lallemand, V. Avantaggiato, M. Maury, A. Simeone & P. Brulet. Forebrain and midbrain regions are deleted in Otx2-/- mutants due to a defective anterior neuroectoderm specification during gastrulation. Development 121, 3279-3290 (1995)
54) V. Avantaggiato, A. Torino, W. T. Wong, P. P. Di Fiore & A. Simeone. Expression of the receptor tyrosine kinase substrate genes eps8 and eps15 during mouse development. Oncogene 11, 1191-1198 (1995)
53) G. Gaudino, V. Avantaggiato, A. Follenzi, D. Acampora, A. Simeone & P. M. Comoglio. The proto-oncogene RON is involved in development of epithelial, bone and neuro-endocrine tissues. Oncogene 11, 2627-2637 (1995)
52) L. Robel, M. Ding, A. J. James, X. Lin, A. Simeone, J. F. Leuckman & F. M. Vaccarino. Fibroblast growth factor 2 increases Otx2 expression in precursor cells from mammalian telencephalon. The Journal of Neuroscience 15, 7879-7891 (1995)
51) P. Mercier, A. Simeone, F. Cotelli & E. Boncinelli. Expression pattern of two Otx genes suggest a role in specifying anterior body structures in zebrafish. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 39, 559-573 (1995)
50) A. Simeone, D. Acampora, M. Pannese, M. D’Esposito, A. Stornaiuolo, M. Gulisano, A. Mallamaci, K. Kastury, T. Druck, K. Huebner & E. Boncinelli. Cloning and characterization of two new members of the vertebrate Dlx gene family. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 2250-2254 (1994)
49) V. Avantaggiato, N. A. Dathan, M. Grieco, N. Fabien, D. Lazzaro, A. Fusco, A. Simeone & M. Santoro. Developmental expression of the RET protooncogene. Cell Growth & Differentiation 5, 305-311 (1994)
48) A. Simeone, M. R. D’Apice, V. Nigro, J. Casanova, F. Graziani, D. Acampora & V. Avantaggiato. Orthopedia, a novel homeobox-containing gene expressed in the developing CNS of both mouse and Drosophila. Neuron 13, 83-101 (1994)
47) A. Simeone, A. Duilio, F. Fiore, D. Acampora, C. De Felice, R. Faraonio, F. Paolocci, F. Cimino & T. Russo. Expression of the neuron-specific FE65 gene marks the development of embryo ganglionic derivatives. Developmental Neuroscience 16, 53-60 (1994)
46) A. Kastury, T. Druck, K. Huebner, C. Barletta, D. Acampora, A. Simeone, A. Faiella & E. Boncinelli. Chromosome locations of human Emx and Otx genes. Genomics 22, 41-45 (1994)
45) F. Galimi, G. P. Bagnara, L. Bonsi, E. Cottone, A. Follenzi, A. Simeone & P. M. Comoglio. Hepatocyte growth factor induces proliferation and differentiation of multipotent and erythroid hemopoietic progenitors. J. Cell Biology 127, 1743-1754 (1994)
44) A. Simeone, D. Acampora, A. Mallamaci, A. Stornaiuolo, M. R. D’Apice, V. Nigro & E. Boncinelli. A vertebrate gene related to orthodenticle contains a homeodomain of the bicoid class and demarcates anterior neuroectoderm in the gastrulating mouse embryo. EMBO J. 12, 2735-2747 (1993)
43) E. Boncinelli, A. Simeone, D. Acampora & M. Gulisano. Homeobox genes in the developing central nervous system. Ann. Genet. 36, 30-37 (1993)
42) R. Dono, L. Scalera, F. Pacifico, D. Acampora, M. G. Persico & A. Simeone. The murine cripto gene: expression during mesoderm induction and early heart morphogenesis. Development 118, 1157-1168 (1993)
41) L. Arcioni, A. Simeone, S. Guazzi, V. Zappavigna, E. Boncinelli & F. Mavilio. The upstream region of the human homeobox gene HOX3D is a target for regulation by retinoic acid and HOX homeoproteins. EMBO J. 11, 265-277 (1992)
40) A. Simeone, M. Gulisano, D. Acampora, A. Stornaiuolo, M. Rambaldi & E. Boncinelli. Two vertebrate homeobox genes related to the Drosophila empty spiracles gene are expressed in the embryonic cerebral cortex. EMBO J. 11, 2541-2550 (1992)
39) A. Simeone, D. Acampora, M. Gulisano, A. Stornaiuolo & E. Boncinelli. Nested expression domains of four homeobox genes in developing rostral brain. Nature 358, 687-690 (1992)
38) M. T. Corsetti, P. Briata, L. Sanseverino, A. Daga, I. Airoldi, A. Simeone, G. Palmisano, C. Angelini, E. Boncinelli & G. Corte. Differential DNA binding properties of three human homeodomain proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 20, 4465-4472 (1992)
37) M. Fagioli, M. Alcalaly, P. P. Pandolfi, L. Venturini, A. Mencarelli, A. Simeone, D. Acampora, F. Grignani & P. G. Pelicci. Alternative splicing of PML transcripts predicts coexpression of several carboxy-terminally different protein isoforms. Oncogene 7, 1083-1091 (1992)
36) M. D’Esposito, F. Morelli, D. Acampora, E. Migliaccio, A. Simeone & E. Boncinelli. EVX2, a human homeobox gene homologous to the Even-Skipped segmentation gene, is localized at the 5′ end of HOX4 locus on chromosome 2. Genomics 10, 43-50 (1991)
35) A. Simeone, D. Acampora, V. Nigro, A. Faiella, M. D’Esposito, A. Stornaiuolo, F. Mavilio & E. Boncinelli. Differential regulation by retinoic acid of the homeobox genes of the four HOX loci in human embryonal carcinoma cells. Mechanisms of Development 33, 215-228 (1991)
34) E. Boncinelli, A. Simeone, D. Acampora & F. Mavilio. HOX gene activation by retinoic acid Trends in Genetics 7, 329-334 (1991)
33) G. La Mantia, D. Maglione, G. Pengue, A. Di Cristofano, A. Simeone, L. Lanfrancone & L. Lania. Identification and characterization of novel human endogenous retroviral sequences preferentially expressed in undifferntiated embryonal carcinoma cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 19, 1513-1520 (1991)
32) A. Faiella, M. D’Esposito, M. Rambaldi, D. Acampora, S. Balsofiore, A. Stornaiuolo, A. Mallamaci, E. Migliaccio, M. Gulisano, A. Simeone & E. Boncinelli. Isolation and mapping of EVX1, a human homeobox gene homologous to even-skipped, localized at the 5′ end of HOX1 locus on chromosome 7. Nucleic Acids Res. 19, 6541-6545 (1991)
31) C. B. Oudejans, M. Pannese, A. Simeone, C. J. L. M. Meijer & E. Boncinelli. The three most downstream genes of the Hox-3 cluster are expressed in human extraembryonic tissues including trophoblast of androgenetic origin. Development 108, 471-477 (1990)
30) A. Simeone, D. Acampora, L. Arcioni, P. W. Andrews, E. Boncinelli & F. Mavilio. Sequential activation of HOX2 homeobox genes by retinoic acid in human embryonal carcinoma cells. Nature 346, 763-766 (1990)
29) A. Stornaiuolo, D. Acampora, M. Pannese, M. D’Esposito, F. Morelli, E. Migliaccio, M. Rambaldi, A. Faiella, V. Nigro, A. Simeone & E. Boncinelli. Human HOX genes are differentially activated by retinoic acid in embryonal carcinoma cells according to their position within the four loci. Cell Differentiation and Development 31, 119-127 (1990)
28) A. F. Peverali, M. D’Esposito, D. Acampora, G. Bunone, M. Negri, A. Faiella, E. Migliaccio, A. Simeone, G. Della Valle & E. Boncinelli. Expression of HOX homeogenes in human neuroblastoma cell culture lines. Differentiation 45, 61-69 (1990)
27) L. Cianetti, U. Testa, L. Scotto, R. La Valle, A. Simeone, G. Boccoli, G. Giannella, C. Peschle & E. Boncinelli. Three new class I HLA alleles: structure of mRNAs and alternative mechanisms of processing. Immunogenetics 29, 80-91 (1989)
26) E. Boncinelli, D. Acampora, M. Pannese, M. D’Esposito, R. Somma, G. Gaudino, A. Stornaiuolo, M. Cafiero, A. Faiella & A. Simeone. Organization of human class I homeobox genes. Genome 31, 745-756 (1989)
25) A. Simeone, D. Acampora, M. D’Esposito, A. Faiella, M. Pannese, L. Scotto, M. Montanucci, G. D’Alessandro, F. Mavilio & E. Boncinelli. Posttranscriptional control of human homeobox gene expression in induced NTERA-2 embryonal carcinoma cells. Molec. Reprod. Dev. 1, 107-115 (1989)
24) A. Giampaolo, D. Acampora, V. Zappavigna, M. Pannese, M. D’Esposito, A. Carä, A. Faiella, A. Stornaiuolo, G. Russo, A. Simeone, E. Boncinelli & C. Peschle. Differential expression of human HOX-2 genes along at the anterior-posterior axis in embryonic central nervous system. Differentiation 40, 191-197 (1989)
23) A. Faiella, D. Acampora, M. Pannese, M. D’Esposito, A. Simeone & E. Boncinelli. Organizzazione delle regioni genomiche umane codificanti omeodomini. Atti Acc. Lincei Rend. fis. LXXXIII 8, 293-298 (1989)
22) A. Ciccodicola, R. Dono, S. Obici, A. Simeone, M. Zollo & M.G. Persico. Molecular characterization of a gene of the “EGF family” expressed in undifferentiated human NTERA2 teratocarcinoma cells. EMBO J. 8,1987-1991 (1989)
21) D. Acampora, M. D’Esposito, A. Faiellla, M. Pannese, E. Migliaccio, F. Morelli, A. Stornaiuolo, V. Nigro, A. Simeone & E. Boncinelli. The human HOX gene family. Nucl. Acids. Res. 17, 10385-10402 (1989)
20) F. Mavilio, A. Simeone, E. Boncinelli & P. W. Andrews. Activation of four homeobox gene clusters in human embryonal carcinoma cells induced to differentiate by retinoic acid. Differentiation 37, 73-79 (1988)
19) E. Boncinelli, R. Somma, D. Acampora, M. Pannese, M. D’Esposito & A. Simeone. Organization of human homeobox genes. Hum. Reprod. 3, 880-886 (1988)
18) A. Simeone, M. Pannese, D. Acampora, M. D’Esposito & E. Boncinelli. At least three human homeoboxes on chromosome 12 belong to the same transcription unit. Nucleic Acids Res. 16, 5379-5390 (1988)
17) A. Simeone, F. Mavilio, D. Acampora, A. Giampaolo, A. Faiella, V. Zappavigna, M. D’Esposito, M. Pannese, G. Russo, E. Boncinelli & C. Peschle. Two human homeobox genes, c1 and c8: structure analysis and expression embryonic development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 84, 4914-4918 (1987)
16) D. Acampora, M. Pannese, M. D’Esposito, A. Simeone & E. Boncinelli. Human homeobox-containing genes in development. Human Reproduction 2, 407-414 (1987)
15) L. A. Cannizzaro, C. M. Croce, C. A. Griffin, A. Simeone, E. Boncinelli & K. Huebner. Human homeo box containing genes located at chromosome regions 2q31-q37 and 12q12-12q13. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 41, 1-15 (1987)
14) G. Sebastio, M. D’Esposito, M. Montanucci, A. Simeone, S. Auricchio & E. Boncinelli. Modulated expression of human homeobox genes in differentiating intestinal cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2, 751-756 (1987)
13) A. Simeone, F. Mavilio, L. Bottero, A. Giampaolo, G. Russo, A. Faiella, E. Boncinelli & C. Peschle. A human homeo box gene specifically expressed in spinal cord during embryonic development. Nature 320, 763-765 (1986)
12) F. Mavilio, A. Simeone, A. Giampaolo, A. Faiella, V. Zappavigna, D. Acampora, G. Poiana, G. Russo, C. Peschle & E. Boncinelli. Differential and stage-related expression in embryonic tissue of a new human homeobox gene. Nature 324, 664-668 (1986)
11) E. Boncinelli, A. Simeone, A. Faiella, D. Acampora & L. Scotto. Transcribed homeogenes in man. Cell Biol. Int. Rep. 10, 481 (1986)
10) E. Boncinelli, A. Simeone, A. La Volpe, A. Faiella, V. Fidanza, D. Acampora & L. Scotto. Human cDNA clones containing the homeo box sequences. Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant. Biol. 50, 301-305 (1985)
9) A. La Volpe, A. Simeone, M. D’Esposito, L. Scotto, V. Fidanza, A. de Falco & E. Boncinelli. Molecular analysis of the heterogeneity region of the human ribosomal spacer. J. Mol. Biol. 183, 213-223 (1985)
8) B. Majello, G. La Mantia, A. Simeone, E. Boncinelli & L. Lania. Activation of major histocompatibility complex class I mRNA containing an Alu-like repeat in polyoma virus-transformed rat cells. Nature 314, 457-459 (1985)
7) A. Simeone, A. La Volpe & E. Boncinelli. Nucleotide sequence of a complete ribosomal spacer of D. melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 13, 1089-1101 (1985)
6) A. La Volpe, V. Fidanza, A. de Falco, L. Scotto, A. Simeone & E. Boncinelli. Molecular organization of the heterogeneity region in human ribosomal genes. Bull. Mol. Biol. Med. 9, 27-34 (1984)
5) E. Boncinelli, M. H. Goyns, L. Scotto, A. Simeone, P. Harris, J. E. Kellow & B. D. Young. Isolation of a series of HLA class I clones from a human chromosome 6 genomic library. Mol. Biol. Med. 2, 1-14 (1984)
4) A. Simeone & E. Boncinelli. 5′-cleavage site of D. melanogaster 18S rRNA. FEBS Letters 167, 249-253 (1984)
3) E. Boncinelli, A. Simeone, A. de Falco, V. Fidanza & A. La Volpe. An agarose gel resolving a wide range of DNA fragment lengths. Anal. Biochem. 134, 40-43 (1983)
2) E. Boncinelli, A. Borghese, F. Graziani, G. La Mantia, A. Manzi, C. Mariani & A. Simeone. Inheritance of the rDNA Spacer in D. melanogaster. Mol. Gen. Genet. 189, 370-374 (1983)
1) A. Simeone, A. de Falco, G. Macino & E. Boncinelli. Sequence organization of the ribosomal spacer in D. melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 10, 8263-8272 (1982)
*Co-corresponding author.
Books
3) E. Boncinelli & A. Simeone. Ingegneria Genetica. Editor IDELSON – Napoli, pp. 371 (1990).
2) E. Boncinelli & A. Simeone. Principi di Ingegneria genetica e biologia molecolare del genoma eucariotico, pp. 169.Editor Momento Medico, Salerno, (1984).
1) E. Boncinelli & A. Simeone. Principi di ingegneria genetica e struttura del genoma eucariotico, pp. 77. Editor Momento Medico; Salerno, (1982).
Education
1989 Ph.D in Cellular and Molecular Genetics, University of Naples.
1981 Graduated in Biological Sciences, University of Naples.
Honours and Prizes
2013 Prize “Science Award Stadt Freising” for German-Italy interactive studies on Dopaminergic neurons.
2009 Prize “Stella di Tabor” for studies on neurodegeneration awarded by Archidiocesan Curia and Municipality of Amalfi.
2003 Special Prize “Il Gladiatore d’Oro” awarded to the career by Province of Benevento.
2000 The LILIANE BETTENCOURT LIFE SCIENCES Award for studies on the evolution of the mammalian brain.
1998 Italian Society of Biophysics and Molecular Biology (SIBBM) Prize in memory of “Dr. M. Chiara D’Onofrio” for studies on brain development.
1988 ARFACID prize in memory of Prof. Eduardo Scarano.
1986 Italian Association of Medical Genetics (AIGM) Prize.
Appointments
2019 – ……. Director of the Institute of Genetics and Biophysics “Adriano Buzzati-Traverso”, CNR, Naples
2018 – 2019 Acting Director of the Institute of Genetics and Biophysics “Adriano Buzzati-Traverso”, CNR, Naples
2014 – 2018 Director of the Institute of Genetics and Biophysics “Adriano Buzzati-Traverso”, CNR, Naples
2014 -2016 CNR Representative of the “Comitato di Indirizzo Strategico” related to “Accordo Quadro CNR/Regione Molise”
2013 – 2014 Acting Director of the Institute of Genetics and Biophysics “Adriano Buzzati-Traverso”, CNR, Naples
2004 – 2012 Professor of the Scuola Superiore Europea di Medicina Molecolare (SEMM)
2005 – 2012 Group leader at the CEINGE Biotecnologie Avanzate, Naples
2001 CNR “Dirigente di Ricerca” at the Institute of Genetics and Biophysics “Adriano Buzzati-Traverso”, CNR, Naples.
2000 – 2006 Group leader at the MRC Centre for Developmental Neurobiology (London).
2000 – 2005 Full Professor of Developmental Genetics at the King’s College London.
1997 – 2001 CNR “Primo Ricercatore” at the Institute of Genetics and Biophysics “Adriano Buzzati-Traverso”, CNR, Naples.
1992 – 2004 Group leader at the Institute of Genetics and Biophysics “Adriano Buzzati-Traverso”, CNR, Naples.
1988 – 1997 CNR “Ricercatore” at the Institute of Genetics and Biophysics “Adriano Buzzati-Traverso”, CNR, Naples.
Editorial activities
- Member of the editorial board of, and International Journal of Developmental Biology and Development
- Previously member of the editorial board of Human Reproduction, Molecular Reproduction and Development, and Genes and Function.
- Reviewer for Nature Neuroscience, Nature Genetics, Developmental Cell, Genes and Development, Neuron, Developmental Biology, Mechanisms of Development, The Journal of Neuroscience, Stem Cell Reports, PLoS Genetics.
Professional body membership
- Scientific Advisory Board of the Max Planck Institute for Biophysical Chemistry (Gottingen)
- European Molecular Biology Organization (EMBO)
- European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE)
- Italian Society of Biophysics and Molecular Biology (SIBBM)
- Fellowships committee of Human Frontier Science Program Organization (HFSP)
- Armenise-Harvard Italian Scholarship Advisory Committee (ISAC)
- Member of the Scientific Committee of the Foundation Cariplo
Selected Research Projects since 1993
- H2020-MSCA-COFUND Programme (2014-2019) (coordinator): Innovative Life Science PhD Programme in South of Italy (INCIPIT).
- PRIN Project (2017-2020): Regolazione e funzione dei fattori trascrizionali modificatori epigenetici che intervengono nel differenziamento delle cellule staminali embrionali e epiblasti.
- PON MISE Project (2015-2018) (scientific coordinator): Realizzazione di strumenti diagnostici per l’analisi precoce del morbo di Parkinson attraverso l’identificazione di profili genetici di rischio
- PON03 Project (2013-2018): Preclinical development of new therapies and innovative strategies for the production of molecules with pharmacological activity.
- AIRC Project (2013-2016): The Otx2 regulatory network controlling pluripotent stem cell states and their susceptibility to tumorigenesis
- POR MOVIE Project (2012-2015) (research unit): Modelli in vivo models of human pathologies.
- FP7 EU Project (2009-2011): Molecular coding and subset specification of dopamine neurons generating the meso-limbic and nigro-stratal system.
- AIRC Project (2008-2012): Otx genes in medulloblastoma: a genetic study to unravel their role in tumorigenesis of cerebellar progenitors.
- FP6 EU Project (2007-2011): European Transcriptome, Regulome & Cellular Commitment.
- Fondazione Cassa di Risparmio di Roma Project (2007-2010): Ruolo dei geni Otx nel differenziamento e nella proliferazione dei progenitori neurali e delle cellule staminali.
- PRIN Project (2008-2010): Ruolo del gene Otx2 nel differenziamento telencefalico mediante l’uso di modelli murini e cellule ES geneticamente modificati.
- AIRC Project (2005-2007): Otx2 in proliferation and differentiation of neural progenitors: implications for a tumor-suppressor activity.
- FIRB Genotopo Project (2003-2005).
- Wellcome Trust Programme Grant (2001-2005): The role of Otx2 in the evolution of complexity in the vertebrate brain.
- FP5 EU Project (2001-2004): Comparative approach to the analysis of molecular pathways underlying cell communication mechanisms in forebrain patterning
- Medical Research Council (MRC) Programme Grant (2000-2004): Functional Properties of Otx1 and Otx2 in Brain and Sense Organ Development.
- AIRC (1998-2001): Role of Otx and Otp genes in specification of the brain and development of neuroendocrine hypothalamus.
- Telethon Project (1997-2000): Role of Otx1 and Otx2 genes in brain morphogenesis and their involvement in generating epilepsy and otocephaly”.
- Progetto Finalizzato Biotecnolgie (1997-1999): Ruoli e proprietà dei geni Otx nella definizione e evoluzione del cervello e di Otp (Orthopedia) nel differenziamento e funzionalità dell’ipotalamo neuroendocrino.
- AIRC Project (1994-1996): Studio dell’effetto dei fattori di crescita nel differenziamento e nella proliferazione cellulare durante l’embriogenesi e l’emopoiesi.
- AIRC (1993-1994): Ruolo dei geni umani contenenti l’homeobox nel differenziamento e nella trasformazione cellulare.
- Telethon Project (1993-1995): Production of null mutations in the Otx1 and Otx2 homeobox-containing genes: involvement in brain morphogenesis.
- Progetto AIRC (1991-1994): Ruolo dei geni umani contenenti l’homeobox nel differenziamento e nella trasformazione cellulare.
Relevant teaching activity
2004 – 2011: Professor of the Scuola Superiore Europea di Medicina Molecolare (SEMM) at CEINGE Biotecnologie Avanzate site of Naples
2000 – 2005: Professor of Developmental Genetics at the King’s College London.
International Congresses and Seminars
He has participated as speaker in more than 70 International Congresses and also held 200 seminars.
Referral Activities of Research Projects
He was referee for National and International Projects in different Organizations as the Medical Research Council (MRC), the Wellcome Trust, the French National Research Agency (ANR), the Cariplo Foundation, the Banco San Paolo Foundation, the Max Planck and occasionally the ERC.
Scientific interests
1980 – 1984:
- Role of unequal crossing-over in the evolution of ribosomal genes.
- Molecular and structural organization of the non-transcribed spacer (NTS) of ribosomal DNA of D. melanogaster.
- Identification of transcription and processing signals of ribosomal genes of D. melanogaster.
- Isolation and characterization of alternative messenger RNAs coding class I HLA genes.
1985 – 1991:
- Isolation and identification of the structural organization of the human homeobox gene family (HOX Complex).
- Expression analysis of several Hox genes in human embryos.
- Expression analysis of the human Hox Complex in teratocarcinoma cells (N-tera2/D1) upon treatment with retinoic acid and the definition of temporal colinearity concept.
- Molecular mechanism controlling the expression of the HOX Complex gene family in human teratocarcinoma cells (N-tera2/D1).
1992 – 1998:
- Isolation of the murine homologs of the otd and ems homeobox containing genes and analysis of their expression during brain development.
- Isolation and expression analysis both in invertebrate and vertebrate embryos of a new homeobox containing gene named Orthopedia (Otp).
- Isolation and expression analysis in murine embryos of Dlx5 and Dlx6, two murine homologues of the Drosophila Distal-less gene.
- Combined expression analysis of Otx, Emx, Dlx and Otp during development and definition of brain segmentary identities.
- Temporal map during gastrulation of the retinoic acid effect on development and patterning of murine brain.
- Role of Otx2 in the specification of rostral CNS (forebrain, midbrain and anterior hindbrain).
- Role of Otx1 in corticogenesis, pituitary functions and sense organs development.
- Identification of an Otx gene-dosage dependent mechanism required for patterning of developing brain and proper positioning of midbrain-hindbrain isthmic organizer.
- In vivo dissection of Otx1 and Otx2 roles in brain development by using reciprocal knock-in mouse models: definition of extended functional equivalence between OTX1 and OTX2 proteins and the relevance of the Otx1 and Otx2 differential transcriptional control.
1999 – 2005:
- Dissection of Otx2 roles during gastrulation: requirement of Otx2 in the visceral endoderm for specification of anterior identity, and in the early neuroectoderm for maintenance of the anterior identity (forebrain and midbrain).
- Role of Otx1 and Otx2 in brain evolution: functional equivalence between the invertebrate Orthodenticle and the murine OTX1 and OTX2 gene products supports a conserved genetic program of brain development between insects and mammals.
- Role of Orthopedia (Otp) in proliferation, migration and differentiation of the murine neuroendocrine hypothalamus.
- Differential dosage-dependent roles of OTX2 in specifying regional identities and neuronal cell types during brain development.
- Antagonistic role of Otx2 and Gbx2 in regionalization of midbrain and rostral hindbrain.
- Evidence for an Otx2-dependent control of dorso-ventral patterning of the midbrain.
- Role of Otx2 in the control of identity and fate of neuronal precursors in the ventral midbrain.
2006 – 2012
- Otx2 cell-autonomous control of thalamic glutamatergic progenitors.
- Expression complexity of the Otx2 locus: transcriptional, post-transcriptional and translational regulation of Otx2 mRNA isoforms control specification and maintenance of forebrain and midbrain regional identities.
- Role of Otx2 in dopaminergic neurogenesis: dose-dependent, anterior -posterior and dorsal-ventral integrated control by Otx2 regulates proliferation, number and neurotransmitter phenotype of dopaminergic progenitors.
- Role of Otx2 in adult dopaminergic neurons: Otx2 specify post-mitotic neuron subtype identity in ventral tegmental area (VTA) and antagonizes dopaminergic vulnerability to the Parkinsonian neurotoxin MPTP.
- Role of Orthopedia in neurogenesis of diencephalic dopaminergic neurons.
- Role of Orthopedia in migration of diencephalic progenitors fated to populate the telencephalic amygdala.
- Role of Otx1 and Otx2 in initiation and progression of desmoplastic Sonic Hedgehog-dependent medulloblastomas.
- Identification of Otx1 as a selective diagnostic marker of aggressive Lymphomas.
2013 up today
- Role of Otx2 in neurogenesis and regional identity of dorsal midbrain.
- Role of Otx2 in Embryonic Stem Cells (ESCs): Otx2 is an intrinsic determinant required to maintain the ESC metastable state by antagonizing ground state pluripotency and promoting commitment to differentiation.
- Role of Otx2 in Epiblast Stem Cells (EpiSCs): Otx2 stabilizes the primed EpiSC state by suppressing mesendoderm into neural fate switch in cooperation with BMP4 and Fgf2.
- Role of Otx2 in ESC-based induction of telencephalic neurons: Otx2- mediated requirement for specification of dorsal cortical neurons.
- Role of Otx2 in the transition to primed pluripotency: Otx2 controls transition into primed pluripotency by recruiting Oct4 at new enhancers associated to ESC-derived epiblast-like cells (EpiLCs) differentiation.
- Design of a diagnostic kit to predict late onset of sporadic Parkinson’s Disease.
- Role of Otx2 in the direct control of the Nanog pluripotency core factor: through binding to the Nanog promoter, Otx2 controls the integrity of specific ESC sub-type compartments and in vivo the differentiation of the the epiblast lineage.
- Role of Otx2 in metastability: through mutual antagonism, Otx2 and Nanog specify the heterogeneous identity of metastable ESCs and individually predispose ESCs for optimal response to naïve or formative inducing factors.